Javier López Muñoz - Pharmacological interactions of sulforaphane and gabapentin in a murine fibromyalgia-like pain model
18 de febrero 2025
Te invitamos a leer el artículo: "Pharmacological interactions of sulforaphane and gabapentin in a murine fibromyalgia-like pain model", realizado por el Dr. Francisco Javier López Muñoz, quien fue investigador del departamento de Farmacobiología en la Sede Sur del Cinvestav.
Autores: Ik Yahalcab Zamora Díaz, María Eva Gonzalez Trujano, David Martínez Vargas, G. Fernando Moreno PÉrez, Alberto Hernandez Leon, Hugo Fernando Narvaez GonzÁlez, Rosa Ventura Martínez, Francisco Pellicer, Francisco Javier Lopez Muñoz.
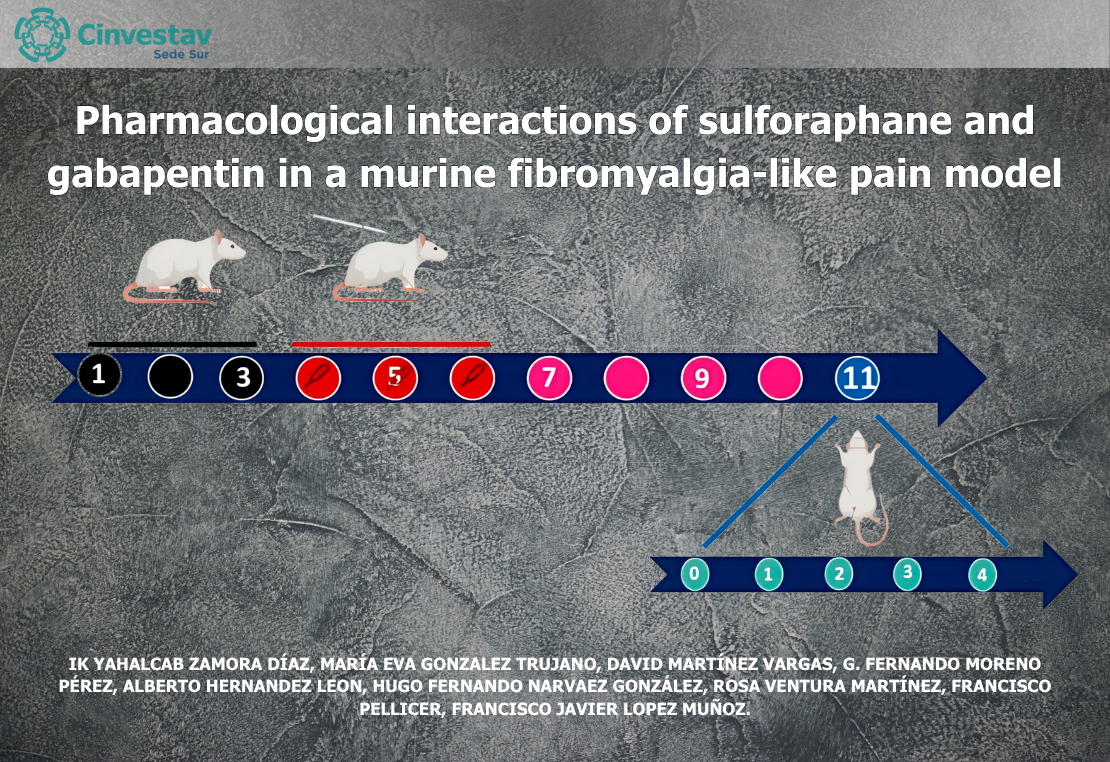
Abstrac: Therapeutic management of a chronic painful syndrome such as fibromyalgia (FM) lacks effective and safe single or combined analgesics. Current medications such as gabapentin (GPB) or pregabalin are moderately effective but in the presence of several adverse effects. Natural products derived from cruciferous vegetables such as sulforaphane (SFN) produce neuroprotective effects due to their potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. However, it is unknown whether positive or negative pharmacological interactions may occur when GBP and SFN are combined. The aim of this study was to estimate the pharmacological interaction of GBP and SFN in FM-like pain induced in rats. Time course curves of antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic effects were constructed for both SFN (3.16, 31.6, and 100 mg/kg, i.p.) and GBP (10, 31.6, and 100 mg/kg, i.p.) by recording behavioral responses every 30 min and up to 4 h afterward, from which dose-response effects were also obtained to decide the dosage combination. An electrocorticographic (ECoG) recording in mice and docking analysis were also explored to explain the pharmacological interaction. Our results demonstrated significant and dosedependent antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic effects in their individual administration. While a combination of intermediate doses of these drugs enhanced their effects producing the same level as that obtained by using only 1/3 of the individual dose in each case. The ECoG recording and docking analysis suggest that calcium channels could be partly involved in the drug interaction. This study provides preclinical evidence that SFN alone and in combination with GBP may be beneficial for relieving FM-like pain at certain doses.
Keywords: Nociplastic pain, Fibromyalgia, Gabapentanoids, Isothiocyanates, Natural products, Synergism.